Hello my dear readers, Welcome to this post. I am your friend, Chandresh Kumar, and today I am writing a little about the recently renamed exam centre, “Adarsh Pariksha Kendra (APK).” Its ...
Our dear readers, a big news is coming from America in which Alphabet’s Google urged the US government to avoid breaking up the firm, this news has been received from the source. It is being tol...
Skype latest news: As you know, Skype offered a convenient and reliable way to make calls and stay in touch. In this era of Zoom, Google Meet and Slack, you may find it hard to believe, but there was ...
What is Grok 3 AI: Friends, it seems that AI is everything in the world, small and big industrialists are busy launching one AI tool after another. DeepSeek’s talk is not over yet that America...
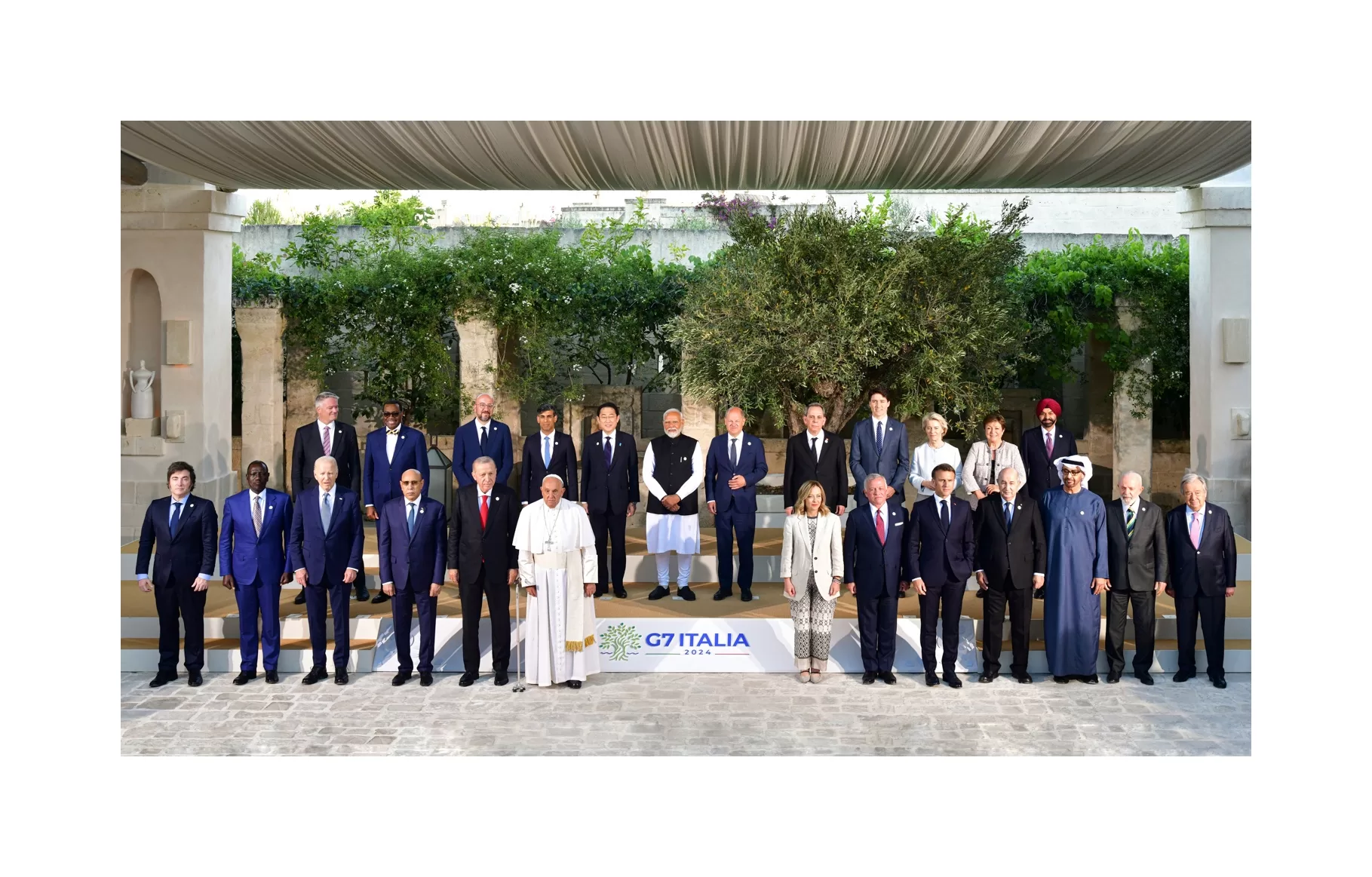
PM Modi-Giorgia Meloni Cheerfulness At G7 Summit. “Hello From Melodi Team” Hello friends, as you all know, Prime Minister Narendra Modi met his Italian counterpart Giorgia Meloni on Friday...
The G7 Summit, short for the Group of Seven, is an annual gathering of leaders from seven of the world’s most advanced economies. This high-profile event provides a forum for discussing and coor...
Introduction Narendra Modi, the 14th Prime Minister of India, has been a transformative figure in Indian politics since he took office on May 26, 2014. Known for his charismatic leadership and ambitio...
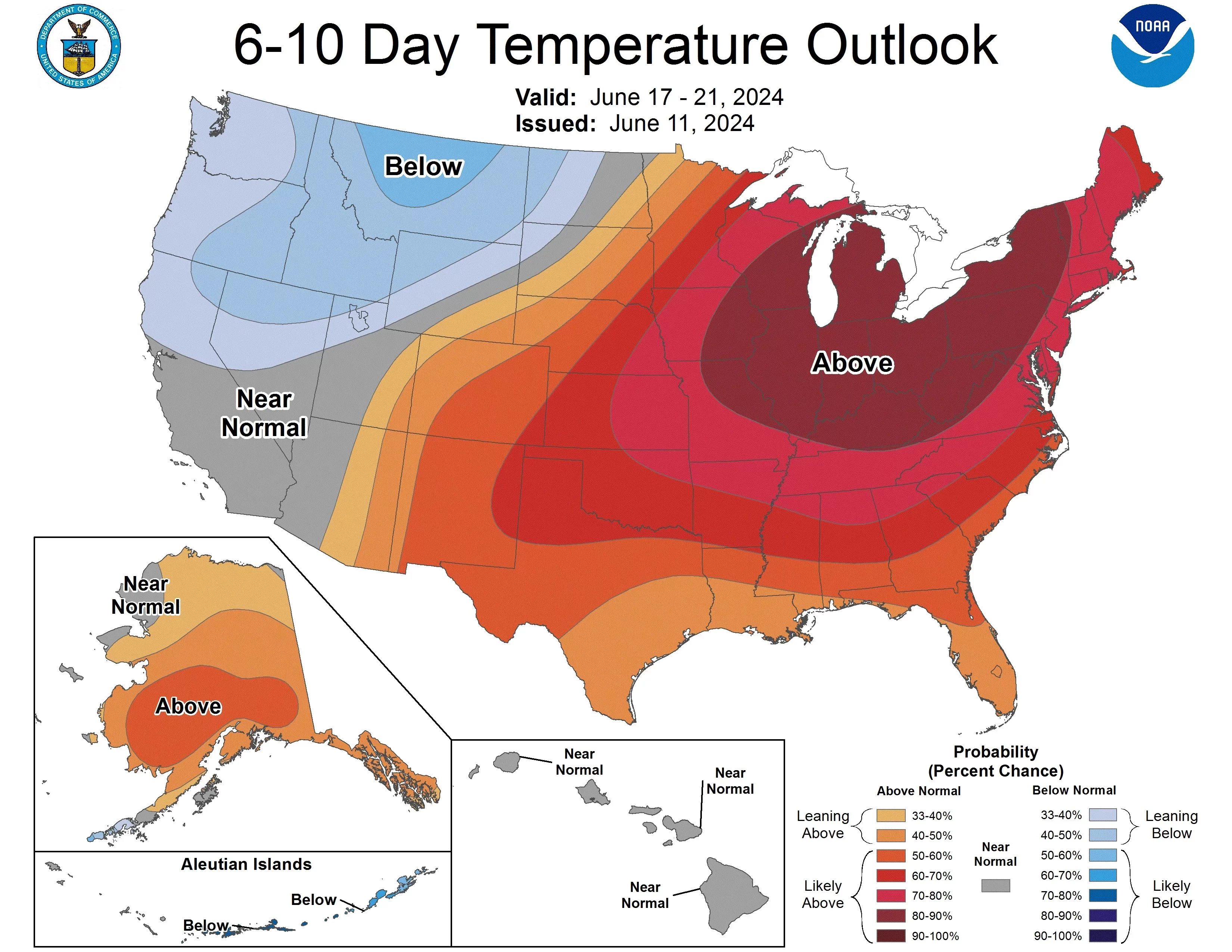
Massive Heat Wave USA Next Week: Friends, the heat wave is increasing day by day. According to a recent report, meteorologists have warned that next week, most parts of central and eastern America wil...
ATES POST Read More...