Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology; Minister of State (Independent Charge) Earth Sciences; MoS PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space, Dr Jitendra Singh announces India’s first indigenously developed vaccine, “CERVAVAC” for the prevention of cervical cancer.
Announcing the scientific completion of the quadrivalent Human Papilloma Virus (qHPV) vaccine in presence of Mr. Adar C. Poonawalla, CEO, Serum Institute of India, Pune and other prominent scientists and dignitaries, Dr Jitendra Singh said, this affordable and cost- effective vaccine marks an important day for DBT and BIRAC as it takes India a step closer to PM Modi’s vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Dr Jitendra Singh pointed out that Cervical cancer ranks as the 2nd most prevalent cancers in India and accounts for nearly one-fourth of the world’s cervical cancer deaths despite being largely preventable. He said, current estimates indicate that every year approximately 1.25 lakhs women are diagnosed with cervical cancer, and over 75 thousand die from the disease in India, and 83 % of invasive cervical cancers are attributed to HPVs 16 or 18 in India, and 70% of cases worldwide. The Minister said, the most promising intervention for preventing cervical cancer is vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV). It is estimated that HPV types 16 and 18 (HPV-16 and HPV-18) together contribute to approximately 70% of all invasive cervical cancer cases worldwide.
Dr Jitendra Singh pointed out that COVID has awakened us to the virtues of preventive healthcare, particularly in a society like India having less awareness of preventive Medicare due to various socio-economic factors. He said, thanks to schemes like Ayushman, which allowed the poor, lower section of the society and the vulnerable population to indulge in the luxury of preventive medicine and preventive healthcare by getting insurance coverage of up to Rs 5 lakh.
Referring to Modi’s visit to Zydus Biotech Park in Ahmedabad, Bharat Biotech in Hyderabad and Serum Institute of India in Pune in November, 2020, to personally review the vaccine development and manufacturing process for Covid, Dr Jitendra Singh said, Prime Minister then underlined that “India considers vaccines as not only vital to good health but also as a global good, and it is India’s duty to assist other countries, including the nations in our neighbourhood, in the collective fight against the virus”.
Dr Jitendra Singh pointed out that within a year of implementation, the Mission Covid Suraksha demonstrated major achievements such as (i) Development of the World’s first DNA Vaccine for COVID-19 by Cadila Healthcare which received Emergency Use Authorization on 20 August 2021, and (ii) Supporting the development of the nation’s first mRNA Vaccine and intranasal vaccine candidate against COVID-19. He said, ‘CERVAVAC’ is an outcome of a partnership of DBT and BIRAC with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, supported by Serum Institute of India Private Limited for the indigenous development of quadrivalent vaccine through its partnership programme ‘Grand Challenges India’. He said, academia, industries and research should become equal partners in the true spirit of Integrated Approach for result-oriented products.
The Minister said that the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has made strenuous efforts to strengthen the Indian vaccine research and development over the past three decades. He added that a number of key initiatives are currently being implemented to promote basic and translational vaccine research, including the (i) Indo-US Vaccine Action Programme, (ii) National Biopharma Mission, (iii) Ind-CEPI Mission, and (iv) Mission COVID Suraksha, which was launched as part of Atmanirbhar Bharat 3.0, with the goal of bringing safe, efficacious, affordable and accessible indigenous COVID 19 vaccines to the citizens of the country at the earliest.
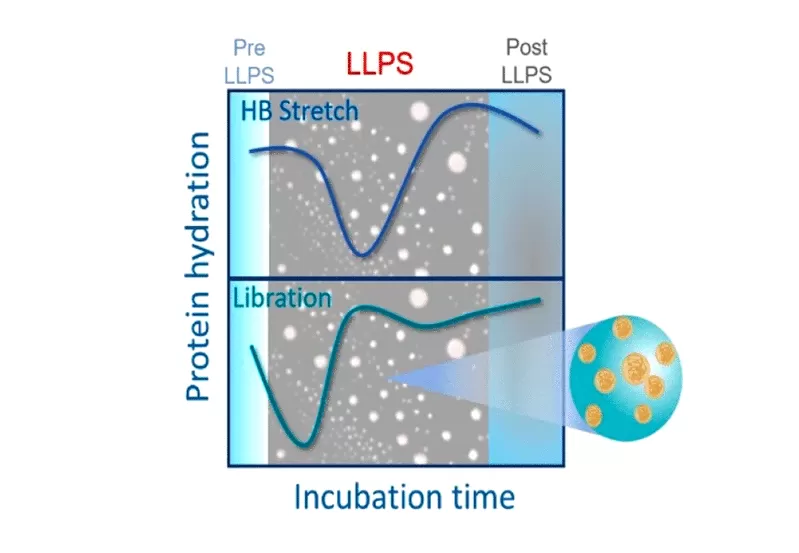
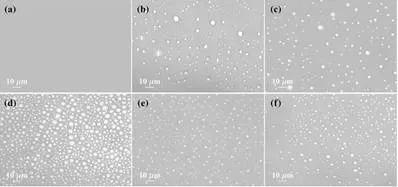
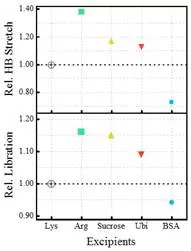
Read Also: Hydration of proteins could act as a potential marker for an early detection of neuro-degenerative diseases
Dr Rajesh Gokhale, Secretary, DBT said, this is a celebration of collective efforts of all stakeholders and added that partnerships with industries are becoming incredibly important for doing R&D, which requires huge funding. He said, India will take a lead in vaccine development and medicine by breaking all barriers for betterment of mankind.
Dr N. Kalaiselvi, DG, CSIR in her address said that the cancer vaccine will help Indian women and women across the globe in major way and we may see in near future the version 1, 2 and 3 of “CERVAVAC”, as technologies are short lived. She said, “India Can Do” and added that we will come out with Indian solutions to Indian problems in true spirit of Atmanirbharta.
Mr. Adar C. Poonawalla, CEO, Serum Institute of India, Pune said in his brief address said that well being and protection of mother and child is the core philosophy of Serum Institute as only a healthy India can be a productive India. He also supported DBT’s vision for more collaboration between Private and Government sectors for manufacturing of vaccines and drugs in India.
Noted film actress Manisha Koirala, who bravely fought and won the battle against ovarian cancer joined virtually to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology and particularly DBT for reaching this milestone. She said, this a great day for women in India and women world over, as there is life beyond cancer. She said, cost effective preventive treatment will inspire millions of such patients to say “Yes to Life”.
Dr. Alka Sharma, Senior Adviser, DBT and MD, BIRAC gave the welcome address, while Dr Shirshendu Mukherjee, Mission Director, Grand Challenges India and In-Charge, Mission COVID Suraksha, BIRAC delivered the vote of thanks.
Dr. Neerja Bhatla, Prof., Gynaecology and Obstetrics, AIIMS, New Delhi, Dr. N. K. Arora, INCLEN Trust, New Delhi, Dr. Umesh Shaligram, Executive Director, Serum Institute of India, Pune, Dr. Guruprasad R. Medigeshi, Asst. Prof., THSTI, Faridabad, Dr. Devasena Anantharaman, Scientist, RGCB, Thiruvananthapuram also took part in the event.